Routine Eye Exams
Importance of Regular Eye Exams

The American Academy of Ophthalmology recommends that most people have an eye exam every one to two years depending upon age and health. An annual eye exam is one of the most important diagnostic and preventative measures you can take to protect your vision and health. If you are in a higher-risk category for eye disease or complications your eye doctor may recommend more frequent exams. If you notice a change in your vision or receive an injury to your eye, you should contact your eye care professional immediately.
While this information is helpful, it should not be construed as medical advice. For more detailed explanation on any of these topics, please consult your eye care professional.
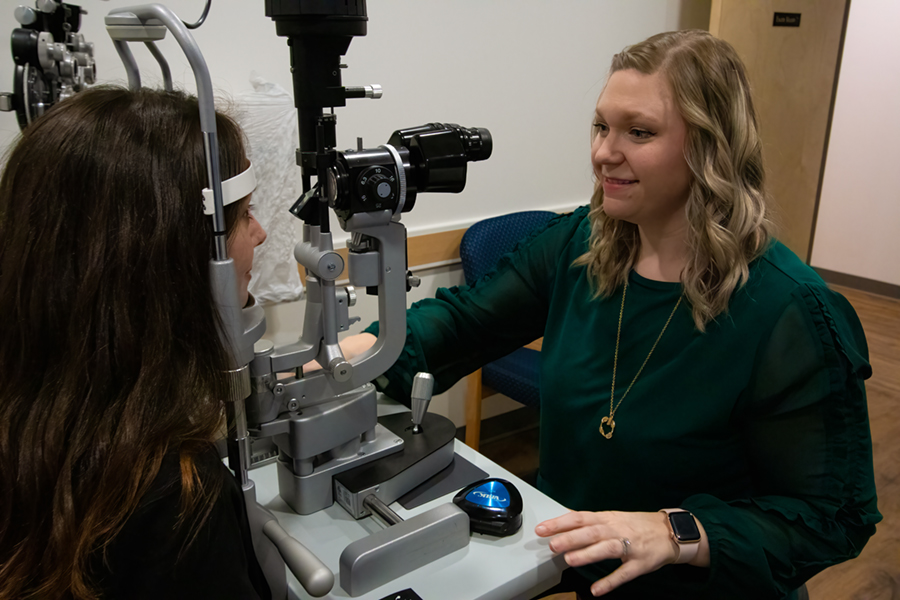
Eye Care Northeast offers a technologically advanced experience for our patients for routine and medical eye examinations. We offer the latest in computerized vision equipment to quickly and comfortably assess your glasses or contact lens needs. Our Certified Ophthalmic Assistants and Technicians will professionally and skillfully guide you through the testing that is necessary before seeing one of our physicians.
Eye Exams
Prescription Glasses and Contact Lenses
You can be comforted to know that we will give you the best prescription of contact lenses or glasses for your needs. Our physicians will also advise you about the different types of lenses available so that you may determine what is best for you or your child.
Slit Lamp
The biomicroscope, or slit lamp, is a vital tool in the examination process. It is a special microscope used with a high-intensity light source that can be focused to shine as a slit or left unfocused to provide general illumination. Our physicians use the slit lamp to see the different parts of the eye in extensive detail.
Intraocular Pressure (IOP)
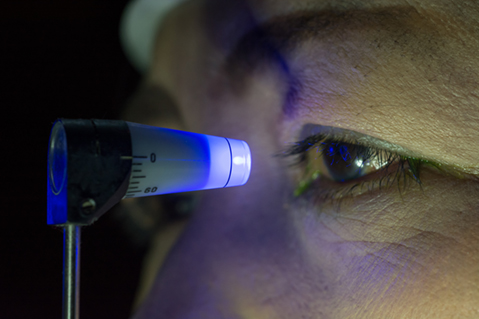
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is a measurement that measures the amount of pressure of the liquid inside the eye. This is often referred to as the “glaucoma test” since having too much pressure inside the eye is a risk factor for glaucoma. However, this is just one test that doctors use to determine whether or not a patient has glaucoma. Glaucoma is a disease of the optic nerve, which is the cable that connects the eye to the brain. In glaucoma, the high pressure inside the eye damages the optic nerve and can lead to blindness if not treated. Most patients usually notice no symptoms during early stages of glaucoma, that is why eye doctors measure the pressure inside the eye during a comprehensive eye examination. Glaucoma is treated by prescription eye medications and several types of surgeries. During tonometry, the eyes are first numbed with anesthetic drops. Our physicians use the “gold standard” of eye pressure measurements, called applanation, which involves contacting the cornea with a pressure-sensing device, illuminated by a blue light. The patient doesn’t feel anything and the process takes only a few seconds. The measurements provided by this examination are instrumental in determining whether or not additional testing for glaucoma is warranted.
Refractive Examination
The refractive examination is how the doctor determines a glasses prescription. It is the process by which the doctor determines what lenses help you achieve your best visual acuity. Your “visual acuity” refers to the clarity of your central vision – how well you see objects in your direct line of sight. Your acuity can be affected by both internal and external conditions.
Pupil Dilation
Dilation of the pupil is important for the inspection of the internal structures of the eye. An examination including dilation can detect serious conditions of the eye, like tumors, retinal detachments, hemorrhages and other conditions that can cause floaters, flashes, or spots appearing suddenly in the vision. There are no pain receptors inside of the eye, so thorough examination with dilation is often the first step in diagnosing a condition that could possibly have devastating effects on your vision.
Without dilation, it is difficult or impossible to determine the health of the retina. It is part of a comprehensive eye examination and is considered standard of care by most eye care providers. During this part of the examination the doctor uses different instruments to evaluate the health of the retina. Often, a binocular indirect ophthalmoscope is used, which is a specialized microscope with a bright light that the doctor wears on his/her head to view the retina. This instrument is valuable for evaluating the periphery of the retina. Many doctors also use a slit lamp and a small lens held in front of the eye to evaluate the central part of the retina.
Due to the widening of the pupil, dilation may cause light sensitivity (usually less than 4 hours, but it may last longer depending upon eye color). Most patients experience difficulty reading for several hours after dilation. While most patients do not have problems driving immediately following dilation, we encourage patients to have a driver with them in case they feel uncomfortable with their vision. You should not operate dangerous machinery until the effects of dilation have worn off. We can reschedule dilation for a more convenient time upon patient request.
Not all patients can be dilated and the doctor will determine the potential for dilation during the examination before dilation is performed.